One reason there are so many open jobs in the USA right now
The very best macro-economic report that helps to shine a light on current labor market conditions is the Bureau of Labor Statistics JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary) report.
The JOLTS report covers job openings, hires, total separations, quits, layoffs, and other discharges, and offers us lots of interesting data points to better understand the US labor market - and by proxy, the health of the US economy.
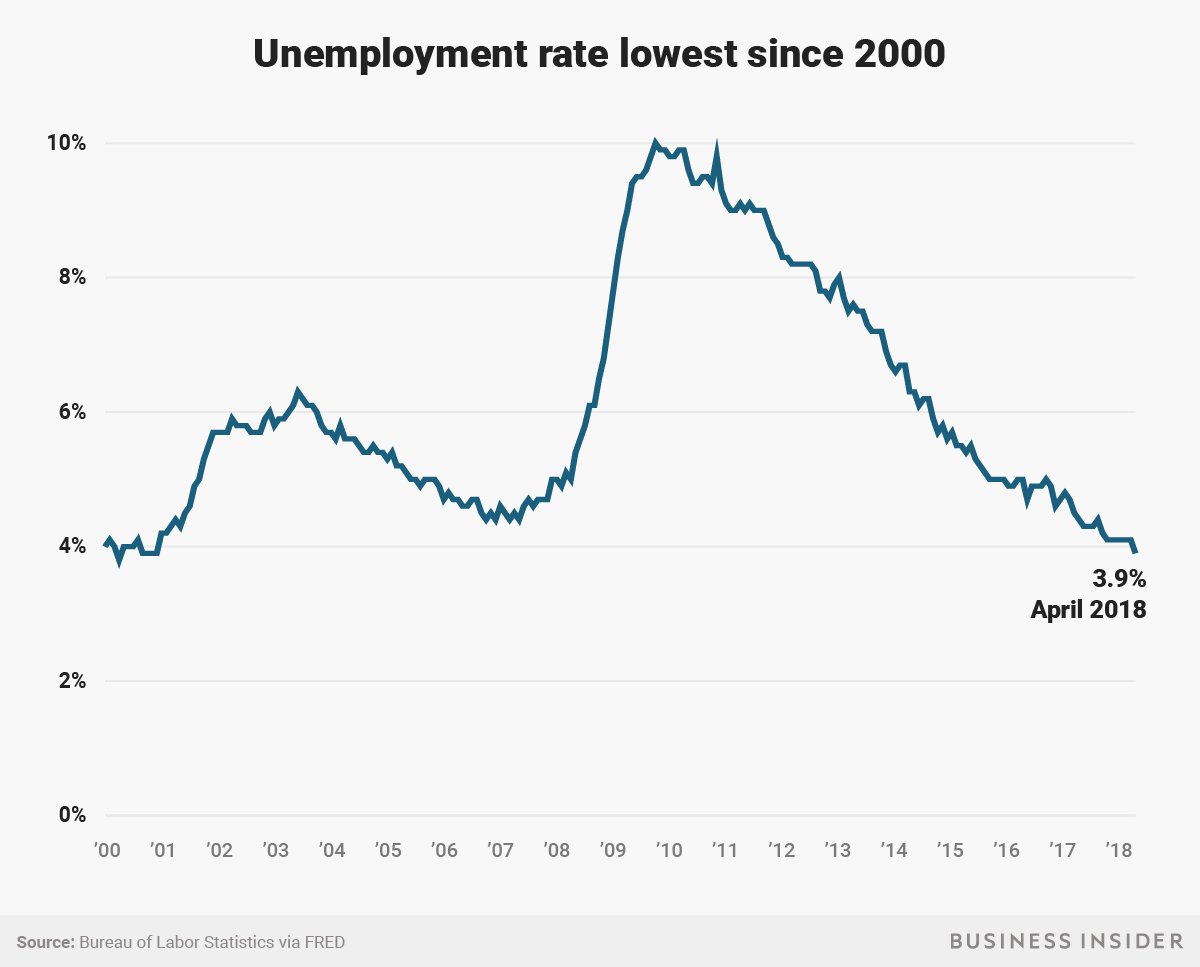
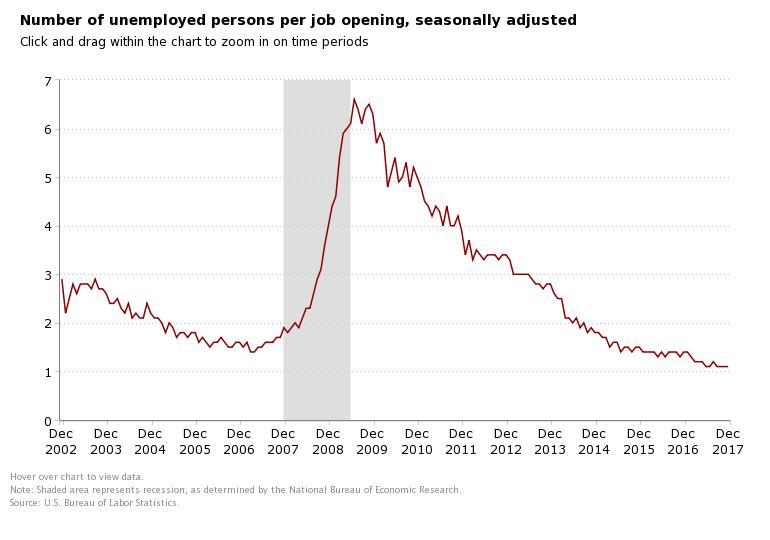
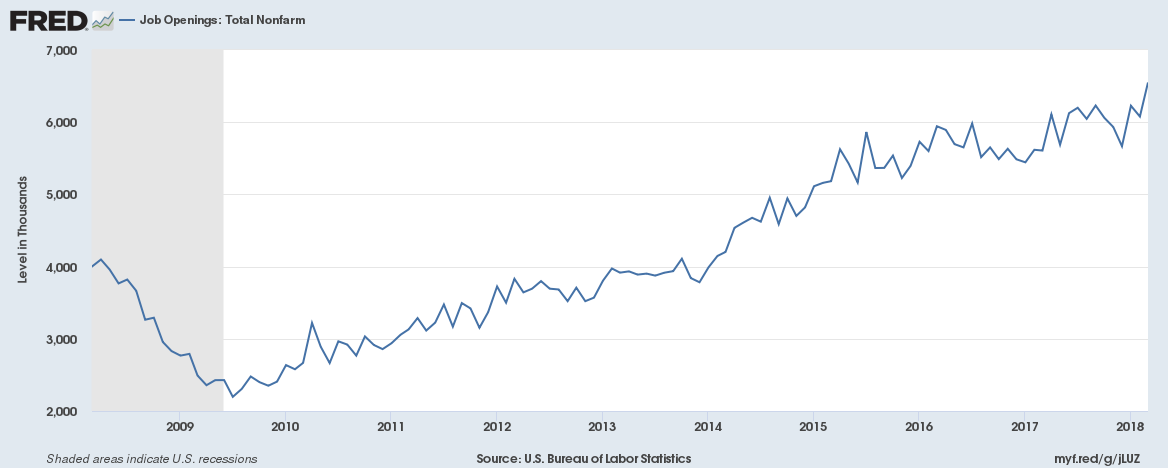
Last month's JOLTS release, on May 8, included one pretty remarkable number in its summary - the number of job openings in the US as of the end of April had risen to 6.6 million - an all time high since the data series began to be compiled in 2000. 6.6 million open and unfilled jobs. That is a lot of openings. No wonder every time I go out I see a bunch of 'Help Wanted' signs.
Jobs stay open, or perhaps better said, remain unfilled, for a whole bunch of reasons - most of them pretty good reasons. Taking time to sort, screen, and interview candidates; trouble finding the right skill set for specific roles; companies taking the extra steps to really be sure a candidate is a good fit before making a hire - these and more are all decent reasons why jobs stay open.
But I have another reason, and some research, I want to point you to that is another reason why some jobs remain open, and open longer than perhaps they should be. It's the concept of 'degree inflation' - the tendency of employers to require that candidates possess more advanced educational degrees than the job function truly requires, and that many candidates simply do not have.
Over the weekend I read a really interesting report on the subject of degree inflation, what it means, where and how often it is occurring, how it negatively impacts the organization, and finally, offering some suggestions for employers to avoid unnecessary degree inflation when hiring.
The report, titled 'Dismissed by Degrees: How degree inflation is undermining U.S. competitiveness and hurting America's middle class'by authors Joseph B. Fuller and Manjari Raman, both from the Harvard Business School, is an interesting and deep look at just what happens when companies try to use artificial degree requirements as a screening tool and a proxy for candidate skills and suitability for a given role.
This is a long report, and I definitely encourage you take some time and read it through, but here are the top three most interesting points or pull quotes from the study that I want to share.
1. In an analysis of more than 26 million job postings, we found that the degree gap (the discrepancy between the demand for a college degree in job postings and the employees who are currently in that job who have a college degree) is significant. For example, in 2015, 67% of production supervisor job postings asked for a college degree, while only 16% of employed production supervisors had one.
2. Seeking college graduates makes many middle skills jobs harder to fill, and once hired, college graduates demonstrate higher turnover rates and lower engagement levels. A systemic view of the total economics of hiring college graduates shows that companies should be extraordinarily cautious before raising credential requirements for middle skill positions and should not gravitate toward college graduates based only on a vague notion that it might improve the quality of their workforce.
3. Degree inflation particularly hurts populations with college graduation rates lower than the national average, such as Blacks and Hispanics, age 25 years and older. In addition, degree inflation raises the barriers to entry for Opportunity Youth, the nearly six million young adults who are currently not in school or in jobs. Companies that insist only on a college degree deny themselves the untapped potential of eager to work young adults as well as experienced, older workers as pools of affordable talent.
Really interesting and plenty to think about in just those three short pull quotes from the report. Even when current holders of a given role in the organization largely do not hold college or advanced degrees, many companies try to require said degrees for new hires into the same role. Then when companies do manage to hire candidates that are say, 'over-degreed' for a role they have to pay them more, the new hires are less engaged, and are more likely to leave - driving up costs and starting the entire process all over. And finally, imposing artificial degree requirements on roles effectively screens out groups of candidates disproportionately and may make any organizational diversity hiring initiatives even harder to progress.
The conclusion of the report does offer some solid suggestions to reduce or eliminate the degree inflation tendency, (chiefly having a better understanding of the critical skills and competencies needed to perform in a given role, and a broader understanding of how candidates can demonstrate these skills), I won't run through them all here, but take a few minutes to read through them as I think most organizations can pretty easily take steps to better understand this issue and make adjustments and changes to their hiring practices.
There are 6.6 million job openings in the US right now. I bet a fair number of them have 'Bachelors Degree' listed as a requirement, when, if we were to be honest, it isn't really required.
Have a great day!

 Steve
Steve