What if everything I told you was wrong?
If you are a fan of the video series TED Talks or have been to an HR conference or two in the past couple of years then you are probably familiar, or at least have heard of Harvard psychologist Amy Cuddy. Her work on something called 'power poses' has been the source of one of the most popular TED talks of all time, with something like 35 million views, a bestselling book titled 'Presence: Bringing Your Boldest Self to Your Biggest Challenges', and has been out on the speaking circuit for most of 2016 promoting the book.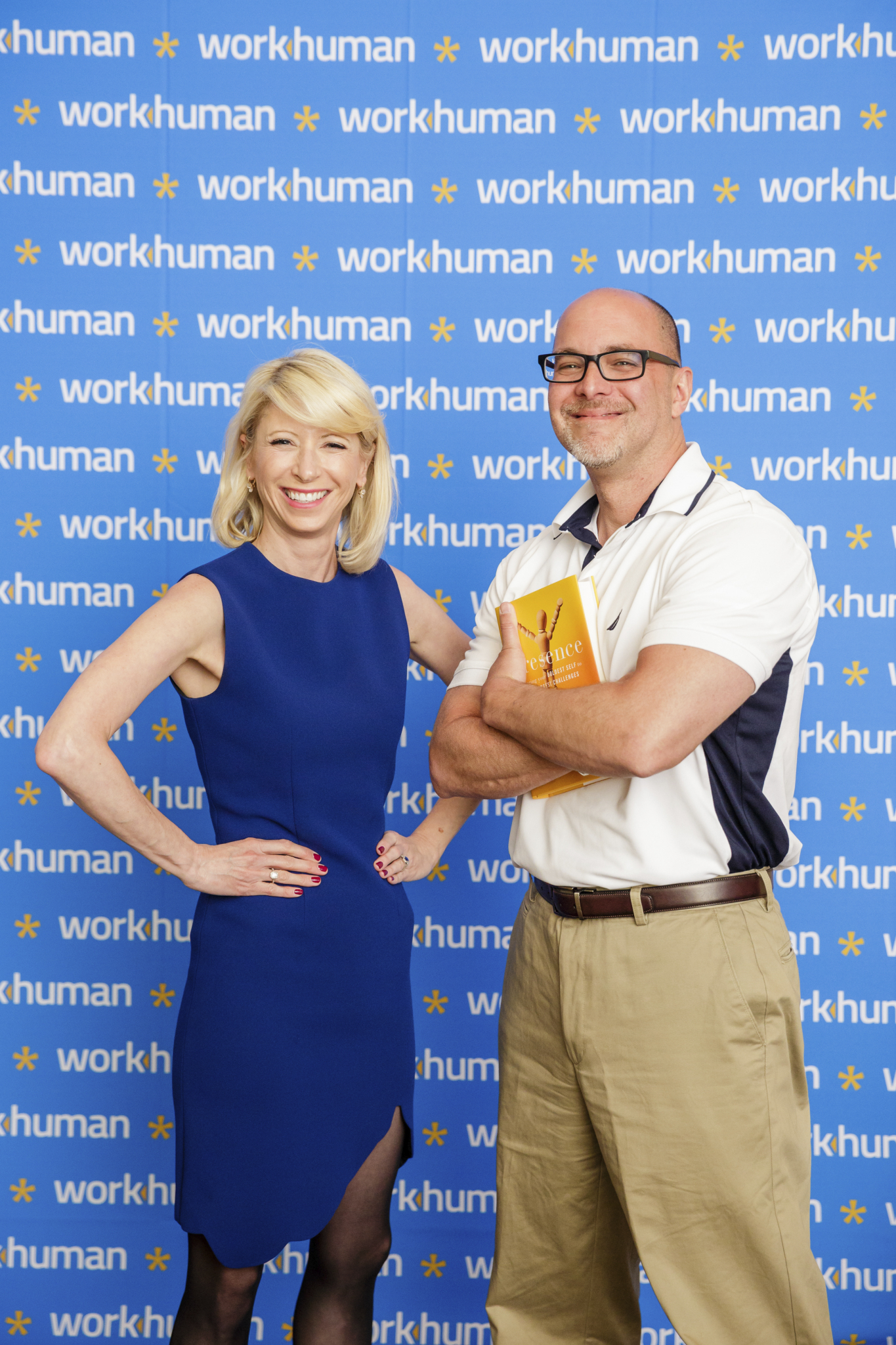 I'm the person not in the power pose
I'm the person not in the power pose
The book's central theses: that leveraging body language in these 'power poses', (think standing tall, arms raised, chin up, chest out, etc.), can help us overcome things like anxiety, fear, lack of confidence and allow us to perform our best, (or at least better), in stressful situations like speeches, job interviews, or presentations. The book, the TED talk, and the speaking gigs all stem from the same source: a 2010 study titled Power Posing: Brief Nonverbal Displays Affect Neuroendocrine Levels and Risk Tolerance authored by Amy Cuddy along with Dana Carney and Andy Yap.
From the 2010 paper's conclusion:
Our results show that posing in high-power displays (as opposed to low-power displays) causes physiological, psychological, and behavioral changes consistent with the literature on the effects of power on power holders—elevation of the dominance hormone testosterone, reduction of the stress hormone cortisol, and increases in behaviorally demonstrated risk tolerance and feelings of power.
It goes on a bit longer, but you get the idea. 'Power poses' can increase testosterone, improve our feelings of power, and help us perform under stress. Awesome to know this, as taking a minute or two to put yourself in a 'power pose' is about one of the easiest things I can think of to do.
But....
What if this actually isn't true? I mean what if the benefits and positive outcomes from adopting 'power poses' are really non-existent, or at least incredibly negliible? What would you think if you have watched Ms. Cuddy's TED talk 26 times, bought and read her book, or paid to attend a conference where she was a keynote speaker?
Remember that 2010 research study at the core of the 'power pose' idea?
Here is what one of the paper's co-authors, Dana Carney has to say today, as reported in Inc.com:
There's only one problem: It (the effects of power poses), isn't real. Several subsequent studies following rigorous protocols were unable to reproduce the effect Cuddy and her co-authors found. Striking a power pose did not increase testosterone, associated with confidence, or decrease cortisol, associated with stress in these subsequent tests. And late last night, Dana Carney, one of Cuddy's co-authors on the original paper, published a document disavowing that research.
She, Cuddy, and the other researchers weren't being dishonest, she explains, but they made some significant mistakes in their research. Their sample size of 47 was much too small. The people conducting the experiment mostly knew what outcome was being sought, which has a tendency to skew research results. The testosterone increase might have been caused by a different aspect of the experiment--people were given the opportunity to gamble and some of them won, which also increases testosterone.
Considering all that was wrong with the original experiments and the fact that later experiments did not produce the same effect, she writes, "I do not have any faith in the embodied effects of 'power poses.' I do not think the effect is real." She goes on to say that she does not conduct research in this area herself and hasn't in years, nor does she teach the material to her students anymore. And she wants to discourage other researchers from pursuing power poses, which she believes are a dead end.
If you read what Carney published essentially disavowing the research's validity and the follow-on from the marketing of the value of 'power poses' you will come away wondering just how silly it all sounds now.
Standing in the Wonder Woman pose for 45 seconds will actually make you act and think and seem like ,you know the actual Wonder Woman? That seems kind of dopey.
And it did to me back when I met Ms. Cuddy, (and where I got the pic you see above).
She was one of the featured speakers at a conference I attended earlier this year, and I was invited to go back stage prior to her talk for a meet and great, get a copy of her book, and take a picture. Prior to that day I had not seen her TED talk, and frankly didn't know much, (anything) about her research and the book. I had never heard of a 'power pose'.
But as I waited in the meet and greet line, I observed 10 or 12 people before me all take a picture with Ms. Cuddy, with the author and the conference attendee each proceeding to adopt the Wonder Woman pose you see Ms. Cuddy in the pic above. As I said, I never heard of the pose, kind of felt idiotic taking up the pose for the pic, and instead stood in what was for me a more comfortable, natural position.
After taking the pic, and talking to some of the folks backstage, I was clued in to just what the Wonder Woman/Power Poses thing was all about. And I felt really stupid that I stood next to the world's foremost expert on Power Posing and took up a pose that (I later learned), was the exact opposite of what I should have done.
I am standing with my arms folded in, am slightly hunched, (Ms. Cuddy is kind of short), and more or less look exactly like someone who had never heard of a Power Pose, and the benefits that such a pose provides.
Long, long story short - I really have no idea if Power Posing creates any real benefit or value or not. I suppose even if it can't be scientifically proven, but it still makes one feel better and seemingly more confident, then it can't hurt.
Just, in the future, if you have Ms. Cuddy speak at your Conference you may want to skip the awkward meet and great posing routine. It did feel dumb to me when I was there. And I'd feel even dumber if I had taken up the Wonder Woman pose only to find out a few months later that it doesn't actually, you know, do anything.

 Steve
Steve